Table of Contents
Topical preparations
- Colloids, liniment, lotions, paints, and some, solution are the preparation applied topically to the skin, douches, ear drops, enemas, irrigations, nasal drops, sprays and other solution alternatively are the preparation instilled into body cavities.
- The container and closures used for these preparation should be different from those used for oral preparations, should be different from those used for oral preparations, colour is the only distinguishing feature between bottle and ribbed oval used for mouthwashes.
- The inhalation preparations to be inhaled or sprayed should be packed in colourless fluted bottles, because the drug is delivered to the respiratory tract.
Ointments
- Ointments are semi solid preparations for external applications to skin or mucous membranes.
- The components of an ointments often but do not melt upon application to the skin.
- They are used topically on a variety of body surface.
- These include the skin and the mucous membranes of the eye (eye ointment), vagina, anus and nose.
Therapeutical Ointments:
- Ointments function as skin protective and emollients, but they are primarily as vehicles for the topical application of drug substances.
- It should be chemically and physically stable.
- It should be smooth and free from grittiness.
Advantages of Ointments
- They are easy to handle than the bulky liquid dosage forms.
- They are directly applied to the target area avoiding the other body parts.
- Patients sensitive to parenteral and oral route prefer ointment.
Disadvantages of Ointments
- They are more bulky than the solid dosage form.
- They required high cost of production.
- They may cause skin irritation.
- They may get contaminated when applied using fingers.
Pastes
- Pastes are the semi solid preparations meant for external applications to the skin. They contain large amount of finely powdered solids like starch, zinc oxide etc.
- Due to presence of these substances they have viscosity and stiffness and less attractive cosmetically. Since paste are stiff they do not melt at ordinary temperature thus forming and holding a protective coating over the area they are applied.
Difference between Ointments and Pastes:
| Sr. No. | Ointments | Pastes |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Less Viscous | More Viscous |
| 2. | Less Stiff | More Stiff |
| 3. | More greasy | Less greasy |
| 4. | Contain less cone of solids | More concentrated than ointment |
| 5. | Oleaginous , water soluble water miscible and absorption bases can be used for preparation. | Except absorption bases all other bases can be used. |
GELS
- Gels are aqueous colloidal suspensions of hydrated forms of medicinal substances for oral administration.
- Gels are used to deliver drugs orally, topically, and via injection. They are formulated by choosing appropriate vehicles, gelling agents, and additives. Gels are prepared via thermal, flocculation, or chemical methods.
- A gel refers to the semi- solid, 3-dimensional matrix formed from an interspersed system of colloidal particles or the permeation of a solvent into an entwined polymer chain network. Pharmaceutical gels are formed by adding a gelator (gelling agent) to the solvent and active ingredient mixture.
Example: Aluminium hydroxide gel, etc.
Cold Cream
- Cold cream is an emulsion which when applied on the skin a cooling effect is produced due to slow evaporation of water present in the emulsion. This are generally prepared by emulsion.
- This are generally prepared by emulsification of oil and water.
- In olden days animals fat vegetable oil was used but vegetable oil have rancid tendency so they replaced by mineral oils.
Liniments
- They are defined as the liquid or semi solid preparations meant for application to the skin.
- They are applied to the skin with friction and rubbing of the skin.
- A liniments should not be applied to broken skin because it may cause excessive irritation.
Examples : Camphor liniments, soap liniments, etc.
Suppositories
- A Suppositories is a medical solid dosage form generally intended for use into the rectum vagina to a lesser extent the urethra after insertion they melt or soft at body temperature where as vaginal suppositories some time called as pessaries are also made as compressed table that disintegrate in body fluid.
Or
- Suppository are semi-solid or solid base dosage form of medicament for insertion into body cavity other than mouth and melt into body temperature.
- They are inserted into rectum, vagina or nasal cavity.
- These produce so formulated that after introduce into rectum vagina or nasal cavity.
- These produce so formulated that after introduce the will either melt or dissolve into cavity fluid to release the medicament.
- Suppository available in different sizes and shape.
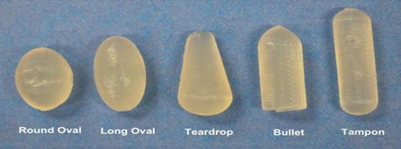
Types of Suppositories
- Rectum suppository.
- Vaginal suppository
- Nasal suppository
- Urethral suppository
- Ear suppository
Advantages of Suppositories
- Drugs are rapidly absorbed in rectal mucosa without ionisation.
- Drugs sensitive to acidic pH of can be administered safety.
- Non – Sedating and bitter drugs can be given in this form without difficulties.
- These can easily administered to children old person and to unconscious patient, who cannot be swallow the drug easily.
- They can be inserted into rectum to rapid active on the rectum.
- These are inserted into rectum to promote evaluation of the bowl.
- Suppository is unit dosage form or drug and no dose variation.
- They have been used to obtained prolonged action of drug.
Disadvantages of Suppositories
- The irritatant drug can’t be administered by this route.
- Absorption of drug through rectum is irregular.
- They are required to be stored self life otherwise throughout there shapes may be destroyed.
- These is leaking problem of material through cavity thus found uncomfortable.
- They should have a maximum disintegration time of 30 minutes.
Pessaries
- They are solid dosage form of medicament meant for introduction into vagina.
- They either melt or dissolve in cavity fluids to release a medicament and exert a local action.
Example: lactic acid, ampicillin, nystatin, etc.
Lotions
- Lotions are defined as the liquid suspensions or dispersions meant for external applications to the skin without friction. They usually contain alcohol and glycerin because alcohol fasten drying and produces cooling sensation where as glycerin keeps the skin moist for a sufficient long time.
Examples: calamine lotions, salicylic acid and mercuric chloride lotions.
Ear Drops
- Ear drops are liquid preparations in which drug or drugs are dissolved or suspended in suitable vehicle like water, dilute alcohol, glycerine and are installed into ear with a dropper.
- They are generally used for clearing ear, drying weeping surfaces, softening the wax and for treating mild infections.
Examples: hydrogen peroxide ear drops, etc.
Nasal Drops
- They are aqueous solutions or liquid paraffin solutions meant for instillation into the nostrills by means of dropper.
- They are commonly used for their antiseptic, local analgesic or vasoconstrictor properties.
Examples: Ephedrine nasal drops.
Rifampin 1% Nasal Drops
Preparation of Nasal Drops

Method of Preparation:
- Calculate the quantity of each ingredient for the amount to be prepared. Accurately weigh or measure each ingredient.
- Heat about 90 mL of the purified water to about 70°C and sprinkle on the hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K4M while stirring.
- After dissolution, cool the mixture to room temperature, add the remaining ingredients, and stir until uniformly dispersed.
- Add sufficient purified water to final volume and mix well. Package and label.
Use:
- Rifampin nasal drops are used in the treatment of susceptible infections in the nasal cavity.
Packaging: Package in nasal-drop containers.
Labeling: Keep out of reach of children. Keep refrigerated. Shake gently. Discard after_____[time period]. For the nose.
Stability: Beyond-use dates of 30 days at room temperature and 76 days at refrigerated temperature have been used.
Quality Control: Quality-control assessment can include weight/volume, pH, specific gravity, active drug assay, color, rheologic properties/pourability, physical observation, and physical stability (discoloration, foreign materials, gas formation, and mold growth).
