Table of Contents
Liquid Oral Preparations
- Liquid oral preparations are medications formulated as liquids intended for oral administration.
- They made of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APis) dissolved or suspended in a suitable liquid medium.
- These preparations are designed to be swallowed, providing a convenient and often fast-acting method of delivering medication.
- They can come in various types, such as syrups, solutions, suspensions, emulsions, and elixirs.
Advantages of Liquid Oral Preparations:
- Easier to swallow: Ideal for infants, children, or people with difficulty swallowing pills.
- Faster absorption: Liquids can dissolve quicker in the stomach, leading to faster medication action.
- Flexible dosing: Easier to adjust dosage for children or those needing smaller amounts.
- Taste masking: Often have added flavors to mask unpleasant medicine taste.
- Soothing effect: Can be soothing for sore throats or coughs (depending on the medication).
Disadvantages of Liquid Oral Preparations:
- Shorter shelf life: Liquids may degrade faster than solid dosage forms.
- Bulky and inconvenient: Can be difficult to store, transport, or measure accurately.
- Risk of spills and contamination: Prone to spills and require careful measurement.
- Not suitable for all medications: Certain drugs may not be stable in liquid form.
- May require refrigeration: Some liquids need to be stored cold.
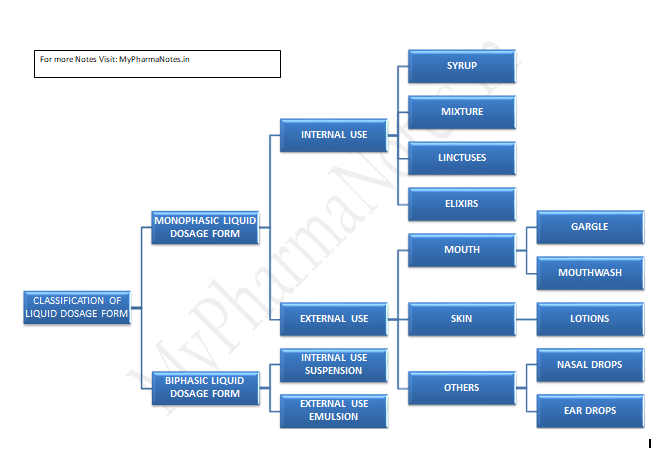
Monophasic
- Monophasic dosage form refers to liquid preparation containing two or more components in one phase system it is represent by true solution.
- The component of the solution which is present in a large quantity is known as “solvent” whereas the component present in small quantity is termed as “Solute”.
Advantage of monophasic
- It is easy to swallow.
- It absorption is faster than Solid
- It can be administered by various routes: Oral, intramuscular, Enema for rectal use etc.
Disadvantages of monophasic
- They bulky so difficult to transport and store.
- Water is commonly use vehicle which is prone to microbial growth. So addition of preservative is need.
- Drug stability reduce by hydrolysis or oxidation.
- They have shorter expire date than Solid dosage form.
Solution
- Solutions are liquid preparations containing one or more drug substances molecularly dispersed in a suitable solvent or a mixture of mutually miscible solvents.
- The two components of a solution are:
- Solvent: It is the phase in which dispersion occurs.
- Solute: It is the phase which is dispersed in the form of molecules or small ions in the solvent
Advantage of Solution
- Easy to Swallow specially for child and geriatric patients.
- Immediate dilution in the GI tract fluids avoids irritation.
- No irritant or toxic effect should be produced by it to the human body
- Flexible dosing according to the weight and age of the patient.
Disadvantages of Solution
- Stability is poor due to hydrolysis.
- Their transportation is not easy because the liquids are bulky in nature.
- Suitable medium for microbial growth.
- Dose accuracy in liquid dosage forms is less than in solid dosage forms.
SYRUP
- They are silent, Viscous, Concentrated solution of sucrose or other sugar in water or any other suitable aquous.
- Syrups are concentrated solutions of sucrose or other sugar to which medicament or flavouring agents are often added.
Classification of Syrup
- Simple Syrup
- Medicated Syrup
- Flavored Syrup
1. Simple syrup
- Simple syrup is concentrated solution of success in purified water. The concentration of sugar is 66% W/W.
- Ex- Ginger syrup, Lemon syrup.
Preparation of simple syrup:
- According to B.P simple syrup is prepared by adding 1Kg of refined sugar to 500ml of boiling distilled water and heating until it is dissolved and adding Boling distilled water until the weight of the whole is 1.5kg.
- The specific gravity of the Syrup should be 1.33.
2. Medicated syrup
- They are aqueous solution Containing sugar and at least one water soluble active ingredient.
- The sugar concentration should be between 65-67%.
- Ex- cough syrup, paracetamol syrup.
3. Flavour Syrup:
- It is typically consist of a simple syrup that is sugar with naturally occurring or artificial (Synthesized) flavour that are also dissolved in them.
- Ex- Coffee, Tea, Cake, Ice-cream etc.
Elixirs:
- Elixirs are clear, pleascently, flavoured, sweetened hydro alcoholic liquid preparations for oral administration.
- The main ingredients of elixers are ethanol and water but glycerine, sorbitol, propylene glycol, flavouring agent, sugar and preservatives may be incorporated to the preparation.
- The elixirs may be medicated or non-medicated.
- The medicated elixirs usually contain very potent drugs such as antibiotics and sedatives.
- The bitter and nauseous test of certain drug can be mask by adding flavouring / sweetening agent.
- The non-medicated elixirs are used as flavours and vehicle (Solvent/liquid).
- Examples are paracetamol elixirs, chloral elixirs.
Storage of Elixirs
- Since elixirs contain alcohol and usually some volatile oils which is contaminate of presence of air and light therefore they should be store in tightly closed, light resistance container and in a cool place.
Emulsions
Emulsion is defined as biphasic liquid dosage form containing a mixture of oil and water and addition of emulsifying agent or emulgent to product emulsion.
Classification of emulsion
A. According to the mode of dispersion
- 0/W ( Oil in water)- oil is an internal phase. Water is external phase ex- milk consists of liquid fat particles dispersed in water.
- W/0 ( Water in oil)- Water is an internal phase. oil is external phase. Emulsion of water in oil. Disperse phase is water and the dispersion medium is oil.
For example, cod liver oil consists of particles of water dispersed in oil.
B. In case of consistency
- Liquid emulsion- usually O/W type and used parenterally orally and externally.
- Semi solid emulsion- this type of emulsion used for external purpose.
C. According to Partical size
- Coarse emulsion
- Micro emulsion
- Fine emulsion
Type of Emulsion
- Water in Oil emulsion (W/O):- In these emulsion rufer to water in oil. If
- the dispersed phase in water and dispersion medium is oil
- Oil in water emulsion (O/W):- These type of emulsion rufer to water oil in oil water in these dispersed phase is oil and dispersion medium is water.
Different between O/W (oil in water) and W/O (water in oil) emulsion
| O/W (oil in water) | W/O (water in oil) |
|---|---|
| 1) Water is the dispersion medium and oil is the dispersed phase. | Oil is the dispersion medium and water is the dispersed phase. |
| 2) non greasy and easily removable from the skin. | Greasy and not water washable. |
| 3) Preferred for internal use as bitter taste of oils can be masked. | Preferred for external use like creams. |
Formulation of emulsions
Following ingredients are included in the formulation of emulsion.
- Oil phase:- This phase medicament or vehicle is mode up of fixed oil mineral oil, volatile oil or also resin type that is used for preparation of Emulsion.
- Aqueous phase:- Due to increased risk of microbial contamination freshly boiled and cooled purified water are used.
- Antioxidant:- It prevents the oil form getting oxidising during Its shelf like hence It enhance the stability of the oil phase in the emulsion.
- Flavouring agent:- It enhances the palatability of the final product pineapple, orange, chocolate, and mint flavours are commonly used.
- Colouring Agent:- It is used for identifying the preparation and enhancing its aesthetic appeal. Erythrosine tartrazine etc. Colours approved by the food Drug and cosmetic act are used as Colouring Agent.
Biphasic liquid dosage form
Suspension
- It is a dispersed system in which our substance is distributed in discrete unit throughout a second substance Phase.
Or
- A course dispersion in which insoluble solid are suspended in a liquid medium with the help of the suspending agent known as pharmaceutical suspension.
Advantages of Biphasic Liquid Dosage form
- Improve chemical stability.
- Higher rate of bioavailability.
- Drug can be dispense as suspension.
Disadvantages of Biphasic Liquid Dosage form
- Physical unstable
- Sedimentation
- Uniform drug delivery difficult to achieve
- Stability is poor
- Suspension containing diffusible solid and liquid and their preparation.
- Diffusible suspension comprising of light powder that are insoluble are sparingly soluble in the vehicle.
Following of the steps involved in the preparation of suspension containing diffusible solid:
- The solubility of all solid vahical is checked in the mixture.
- Then the amount of vahical is calculated which is required to dissolved any soluble solid.
- All solid weight on a electronic balance.
- Then a small braker all the soluble solid are dissolved in the vahical.
- Vahical is added in small quantity mixed with solid in motor and postal to yield a smooth paste. Other vehicles is added in small amount and mix properly.
- Then the motor is the washing are added to the conical mesered.
- Now the remaining liquid ingredients are added to the mixture in the conical mesered this is because some of this ingredients are volatile which may less while being mixed in the mortar.
Dry Powder For Reconstitution:
You will frequently have the opportunity to reconstitute or compound drugs that are in a dry powder form. These are usually drugs such as antibiotics, which lose their potency in a short period of time after being prepared in a liquid dosage form.
- Establish how much of a drug is contained in a vial or bottle.
- Calculate the powder volume displacement of a reconstituted drug.
- Solve problems related to dry powders.
