Table of Contents
- Immunology is the study of the immune system. The immune system is a host defence system comprising many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects us from infection and disease causes bacteria.
- Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine.
SERA: (Serum)
- The clear, pale yellow liquid that separates from the clot in the coagulation of blood.
- Sera does not contain bacteria or toxins. It contains anti formed in another animal.
- Sera acquired immune immediately and remain a short time. Specific animal by immunization, whole blood collected in, but the serum is a nonspecific mixture obtained after centrifugation.
SERA manufacturing methods:
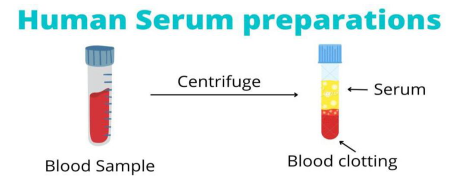
Human Serum preparations
Plasma – Clotting factor= Serum
Antitoxic SERA:
Sera may be Anti-toxic, Anti-viral, Anti-bacterial. Anti-toxic sera more effective than Anti-viral, Anti-bacterial.
Example: Diphtheria Antitoxin:
- It is sterile, nonpyrogenic solution containing specific antitoxic antibody from healthy horse.
- They neutralize the toxin produce by C-diphtheriae Preparation. (c diphtheriae is Corynebacterium diphtheriae. a pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria).
VACCINE
- Vaccine is an antigenic substance prepared from the causative agent of a disease or a synthetic substitute, used to provide immunity against one or several diseases.
- It Contains dead bacteria or weak bacteria or toxins.
- Vaccine stimulates the body to make antioxidants.
- Vaccines are preparations of antigenic materials, which are administered with the objective of inducing in the recipient specific and active immunity against infectious microorganisms or toxins produced by them.
- They contain living or killed microorganisms, bacterial toxoids or antigenic material from the particular parts of bacterum, rickettsia, or virus.
Stages of vaccine production
Vaccine production has several stages. Process of vaccine manufacture has the following steps:
- Inactivation – This involves making of the antigen preparation
- Purification – The isolated antigen is purified
- Formulation – The purified antigen is combined with adjuvants, stabilizers and preservatives to form the final vaccine preparation.
Toxoid Vaccines
- Some bacteria release toxins (poisonous proteins) when they attack the body, and it is the toxins rather than the bacteria itself that we want to be protected against.
- The immune system recognises these toxins in the same way that it recognises other antigens on the surface of the bacteria, and is able to mount an immune response to them.
- Some vaccines are made with inactivated versions of these toxins.
- They are called ‘toxoids’ because they look like toxins but are not poisonous.
- They trigger a strong immune response.
