Table of Contents
Introduction of Manufacturing Plants
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants are facilities where pharmaceutical products are produced. These facilities are designed to meet stringent quality standards to ensure that the products produced are safe and effective for human use.
Basic Structure of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plants
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants are typically designed with a clean room environment that prevents contamination of the products. The facility is divided into different areas such as production areas, packaging areas, quality control areas, and storage areas.
- The basic structure of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant is designed to meet the requirements of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and to ensure that the products produced are safe and effective for human use. The facility is typically divided into different areas, each with its own specific purpose and functions.
- The production areas are designed with a cleanroom environment that prevents contamination of the products. These areas are typically arranged in a linear fashion, with materials flowing from one area to another. The production area is divided into different sections, such as fermentation, synthesis, purification, and drying, each with its own specific functions.
- The formulation section is where the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are formulated into the final product. This section is divided into different areas such as granulation, compression, coating, and packaging.
- The quality control section is responsible for ensuring that the products meet the quality standards. This section is divided into different areas such as chemical analysis, microbiology, and stability testing. The packaging section is responsible for packaging the final product into different forms such as tablets, capsules, and injections.
- The storage section is responsible for storing the raw materials, intermediates, and finished products. This section is designed to provide a controlled environment to ensure the stability of the products
Layout of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plants
- The layout of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant is designed to optimize the flow of materials, people, and equipment to ensure efficiency and minimize the risk of cross- contamination.
- The production areas are typically arranged in a linear fashion with materials flowing from one area to another.
- The layout of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant is also designed to ensure that the facility is compliant with regulatory requirements, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
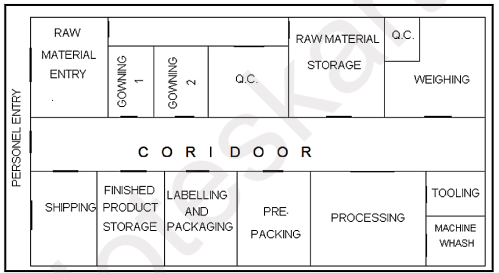
The different areas that are typically included in the layout of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant:
- Raw material storage: This area is used for the storage of raw materials that are used in the manufacturing process.
- Manufacturing/Production areas: These areas are designed for the actual production of the pharmaceutical products. They are typically divided into different sections such as fermentation, synthesis, purification, and drying.
- Formulation area: This area is responsible for formulating the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) into the final product. It may include areas such as granulation, compression, coating, and packaging.
- Quality control area: This area is responsible for ensuring that the products meet the quality standards. It may include areas such as chemical analysis, microbiology, and stability testing.
- Packaging area: This area is responsible for packaging the final product into different forms such as tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Utility areas: These areas are responsible for providing the necessary utilities for the manufacturing process, such as water, air, and electricity.
- Support areas: These areas are designed to support the manufacturing process and may include areas such as maintenance, cleaning, and waste management.
- Administrative areas: These areas are used for administrative and management purposes and may include areas such as offices, conference rooms, and break rooms.
- Storage areas: These areas are responsible for storing the finished products and may include areas such as warehouses and cold rooms.
Sections in a Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plant
The sections of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant are as follows:
- Production Section: This is where the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are manufactured. It is divided into different areas such as fermentation, synthesis, purification, and drying.
- Formulation Section: This section is where the APIs are formulated into the final product. It is divided into different areas such as granulation, compression, coating, and packaging.
- Quality Control Section: This section is responsible for ensuring that the products meet the quality standards. It is divided into different areas such as chemical analysis, microbiology, and stability testing.
- Packaging Section: This section is responsible for packaging the final product into different forms such as tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Storage Section: This section is responsible for storing the raw materials, intermediates, and finished products.
Activities in a Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Plant
The activities of a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant are as follows:
- Raw Material Procurement: Raw materials are procured from approved vendors and are subjected to quality testing before use.
- Production: The production process is carried out in accordance with standard operating procedures (SOPs) to ensure consistency and quality.
- Quality Control: Quality control activities are carried out throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the products meet the quality standards.
- Packaging: The final product is packaged into different forms such as tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Storage: The raw materials, intermediates, and finished products are stored in a controlled environment to ensure their stability.
